| 28
September 2012 |
|
| The
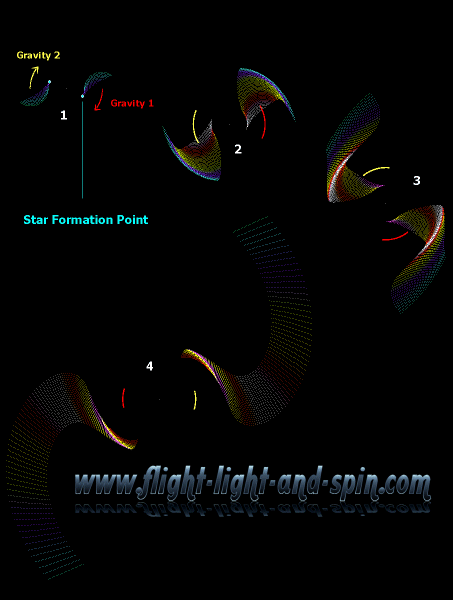
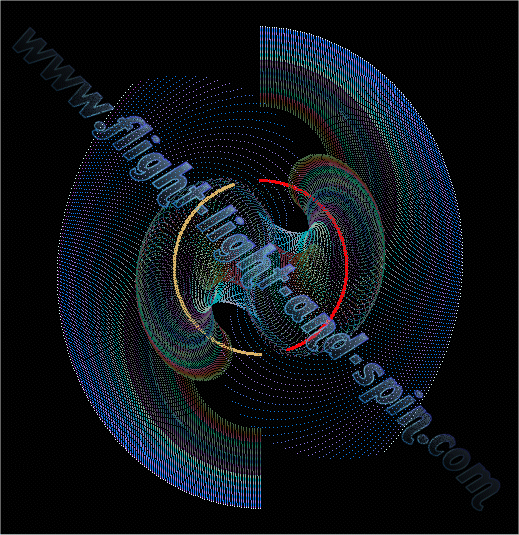
Data Model below explains how Galactical Rotation Curves in Spiral
Galaxies are formed due to twin centers of gravity. Note how there
is no velocity at the middle. The two centers of gravity move slower
than the outer stars. The laws of gravity do not need to be altered
at all. Everything works according to the basic Newtonian law: g=m/r^2 |
|
|
Dark Energy is the innate spin within the early universe. Two objects spinning in unison will overcome their gravitational attraction and sustain circular orbital stability. It is extremely unlikely that a stable spinning pair will form due to randomness. Thus they must have originated from a single spinning object to maintain uniform circularity. Their spin must have become so powerful as to force them apart beyond the pull of gravity. This dynamic nature of the centrifugal force is calculated for planets, stars, galaxies and the Universe as a whole. |
|
Click
the link below and simplified version |
Click
the link below and 4.2 has random variables you can alter |
|
Click
the link below and orbit-game-4-3.exe
demonstrates how the binary pair move away from each other |
| This is how wikipedia outlines the problem: |
 |
| "Left:
A galaxy with a rotation curve as predicted before the effects of dark
matter were known. |
| Compare
this to my data-model: |
| Dark matter has no unique effect on the system. It is just matter that you cannot see. The light at the center of the galaxy is very visible, but it has very little gravitational effect. That is why there is little velocity at the center. The bright light is caused by stars colliding. (Not shown in my model) But, the stars rotating outwards have surpassed escape velocity which is why they do not exhibit the patterns found in solar systems. They recede from the center at a mostlyuniform velocity. |
| here is a full summary of rotation curves of spiral galaxies |
Latest
Article: Gravitational
Waves & General Relativity |
< top >
< seti >
< why? >
< credits >
< contact >
< dark matter >
< dark energy >
< binary orbits >
< the big unwind >
< force of gravity >
< rubin's problem >
< zeno and planck >
< quantum gravity >
< bin laden helicopter crash >
< how the solar system formed >
< rubin's problem solved in animation >
< gravitational waves & general relativity >
< why the moon is receding from the earth >
< calculations of rotation curves of galaxies >
< why the moon is red during a lunar eclipse >
< oscillations in rotation curves of spiral galaxies >
< a full summary of rotation curves of spiral galaxies >